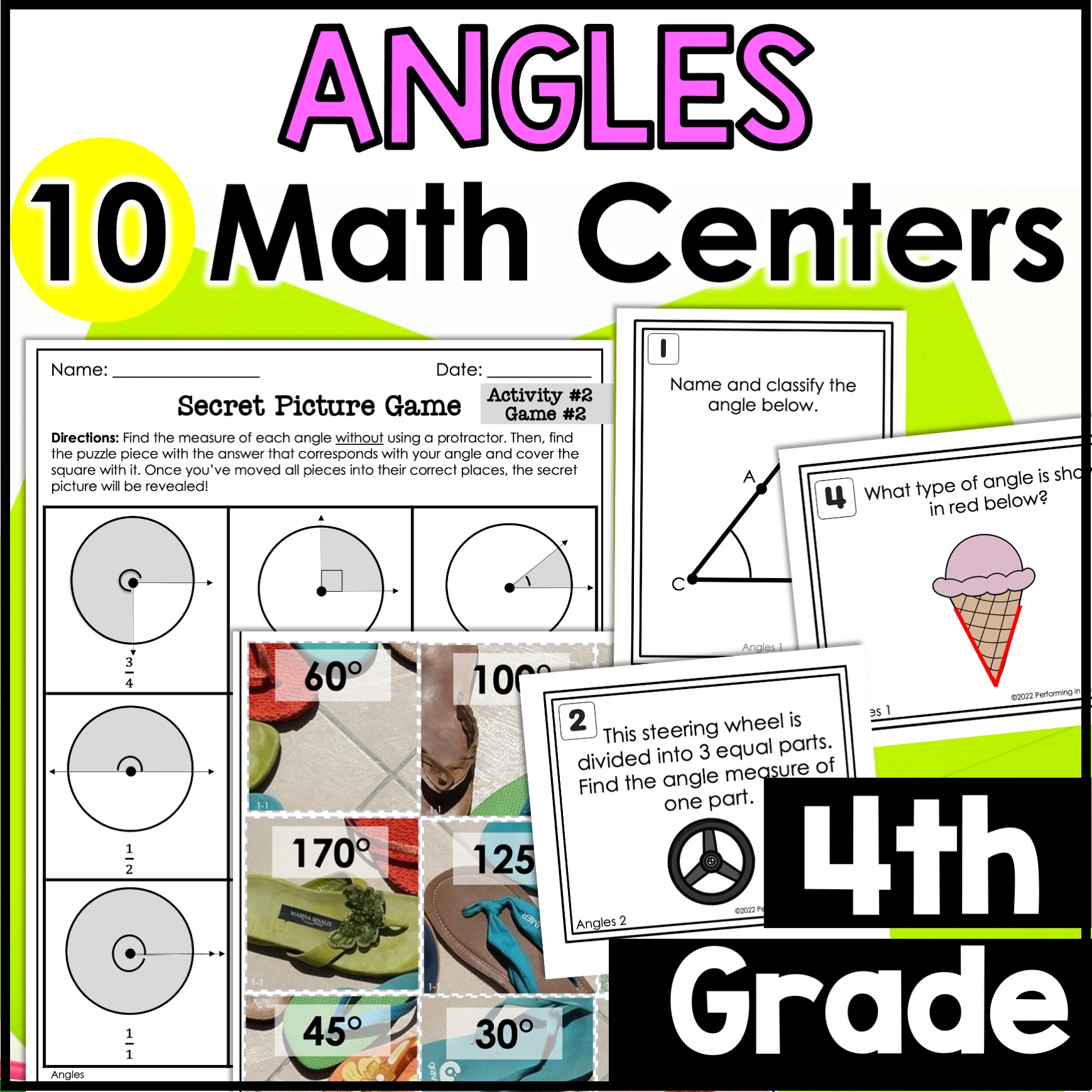
Everything you need to practice angles can be found inside of this set of 4th grade math centers. There are 10 different angles centers included in this set covering naming angles, classifying angles, measuring angles using a protractor, measuring angles using fractional parts of a circle, drawing angles, additive angles, and finding the measurement of an unknown angle.
Along with 10 engaging math centers, this set also includes a teacher guide that walks you through prepping each center, storing your centers, and implementing the centers.
Activities Included:
There are 5 different types of activities included in this set of centers. Each activity includes 2 different centers. Check out the included preview to see an example of each of the math activities below.
- Task Cards
- Board Games
- Error Analysis
- Secret Picture
- Square Puzzles
How to Use These Math Centers:
- Each math center has an answer sheet that can be turned in and graded for student accountability.
- The centers can be reused over and over again. Just prep them once and use them for years to come!
- If you prefer, you can also create single-use centers with the included black and white, printable options.
- The teacher guide includes a printable packet cover page that you can use if you prefer to create weekly math center work packets for your students.
Skills Covered:
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5
Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and understand concepts of angle measurement:
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5.A
An angle is measured with reference to a circle with its center at the common endpoint of the rays, by considering the fraction of the circular arc between the points where the two rays intersect the circle. An angle that turns through 1/360 of a circle is called a “one-degree angle,” and can be used to measure angles.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.5.B
An angle that turns through n one-degree angles is said to have an angle measure of n degrees.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.6
Measure angles in whole-number degrees using a protractor. Sketch angles of specified measure.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.MD.C.7
Recognize angle measure as additive. When an angle is decomposed into non-overlapping parts, the angle measure of the whole is the sum of the angle measures of the parts. Solve addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems, e.g., by using an equation with a symbol for the unknown angle measure.
About the Download:
All of the centers are included in one ZIP download. After unzipping this resource, you will see 6 PDFs: the teacher guide, the task card centers, the board game centers, the error analysis centers, the secret picture centers, and the square puzzle centers. All of the teacher instructions can be found inside of the teacher guide. You will find everything you need for each center inside of the corresponding PDFs.